VAT: BE0688903007 - Cookie privacy
Active at low dose, highly effective
Maximize nutrient utilization
Feed cost savings
Compatible with feed manufacturing conditions
Reduce impact on the environment
Enzymes are added to animal diets consisting of cereal grains (wheat, barley, corn, etc..) to improve dietary, nutritional and energy levels, to maximize nutrient utilization and to reduce feed costs.
Exogenous enzymes improve the nutritional value of feed ingredients by improving the digestion of feeds or by degrading anti-nutritional factors (ANF) such as non‐starch polysaccharides (NSPs), phytate or protease inhibitors that impair the availability of nutrients.
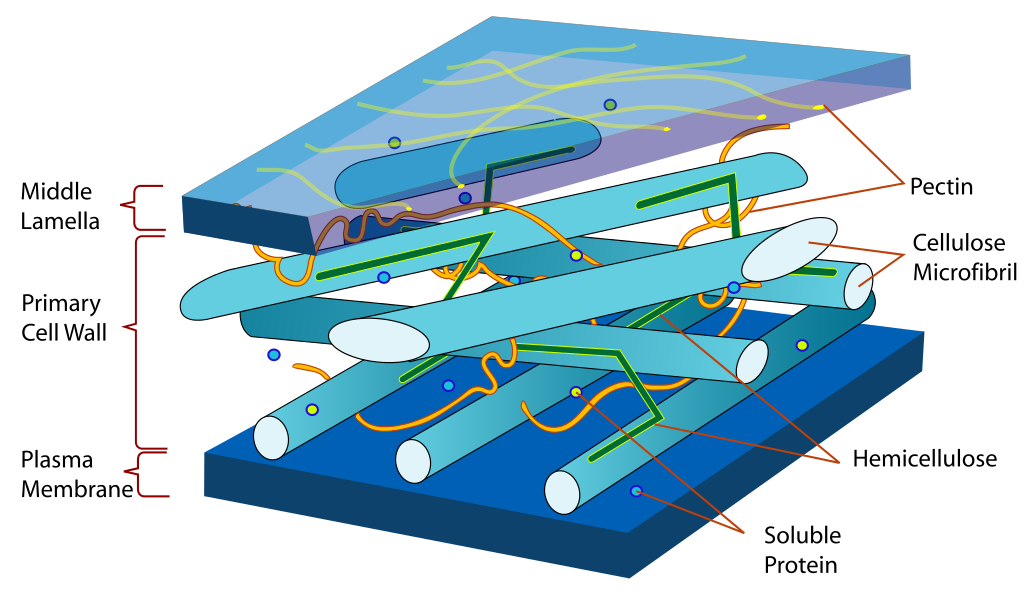
Fiber is indigestible plant matter from cell wall components consisting of non‐starch polysaccharides (NSPs) and lignin.
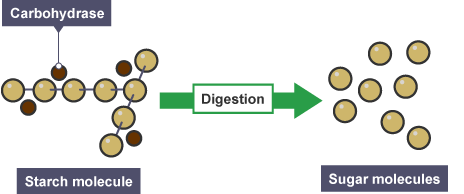
Carbohydrates such as sugars and starch are the primary source of energy in cereals and defatted protein crops. Carbohydrases like α-amylase enzymes catalyze the breakdown of carbohydrates.
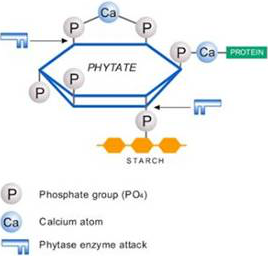
Phosphorus is an essential nutrient that affects growth and reproduction.
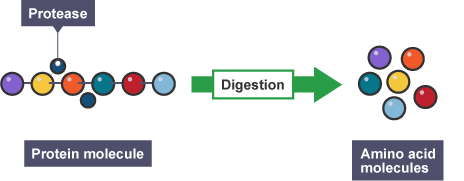
Proteases enhance protein digestion. Endogenous proteases (or peptidases) are secreted by animals for a number of physiological processes, including the digestion of feed protein.
VAT: BE0688903007 - Cookie privacy